
The emblems of Pakistan — the crescent and five-pointed star, the symbols of Islam depicted on the Pakistani flag — merge with the transgender/gender fluidity symbol, which unites the symbols for female, male, and androgynous people.

The term Buraq is derived from an Arabic adjective meaning "lightening" or "magnificently shining." In Islamic tradition, a Buraq is a pegasus-like heavenly creature tasked with flying prophets through the seven planes of sky and back without any time passing on Earth. Most significantly, the Buraq transported the prophet Muhammad during the Night Journey, during which he traveled to Jerusalem and then through the seven heavens before returning to Mecca. There was never a sex assigned to the Buraq, nor is there a single, canonical detailed physical description beyond the basic idea of a bridled creature capable of space and time travel. In South Asia the Buraq is seen as inherently feminine and is described as having the head of a woman; further into the Middle East, it becomes androgynous or masculine. This artwork pays homage to both renditions.

Bindyia's ring is a subtle nod to the Kaaba, the building at the center of Mecca's Masjid al-Haram, Islam's most sacred site, and to the story of how she completed her Umrah pilgrimage. Pilgrims walk around the Kaaba seven times in a counterclockwise direction, a ritual known as Tawaf.

The ongoing danger to the transgender community and the community's resistance are illustrated metaphorically as a dove and a snake.

The dove’s wings are echoed in the design of Bindiya’s sleeves to reinforce her courage and highlight the fight she leads in the battle to eradicate discrimination and violence against the khwaja sirah community.

This Mughal king reminds us of the transgender community’s revered place in the Mughal courts, and of the cultural significance of their stature in the heritage of South Asia. The Mughal Empire lasted from the early 16th to early 18th centuries CE, but transgender identity and culture are documented on the Indian subcontinent as early as the Delhi Sultanate, which began in 1226 CE.
The separate clotheslines in the background hold clothes traditionally worn by women and those traditionally worn by men. Both lines are a part of the landscape, reinforcing the cultural commitment to binary gender and reminding us of the precarious line the khwaja sira community walks.
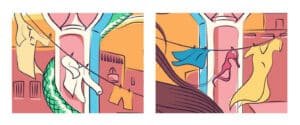
The colors pink, blue, and white are used in Bindiya's garments and in the architecture to represent the transgender pride flag.
